Diamond Education
-
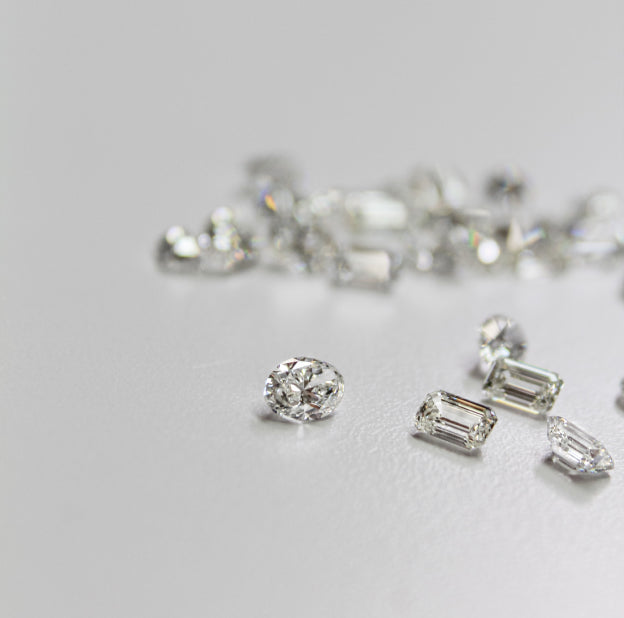

Cut
Cut is determined by how a diamond’s facets interact with light.
-
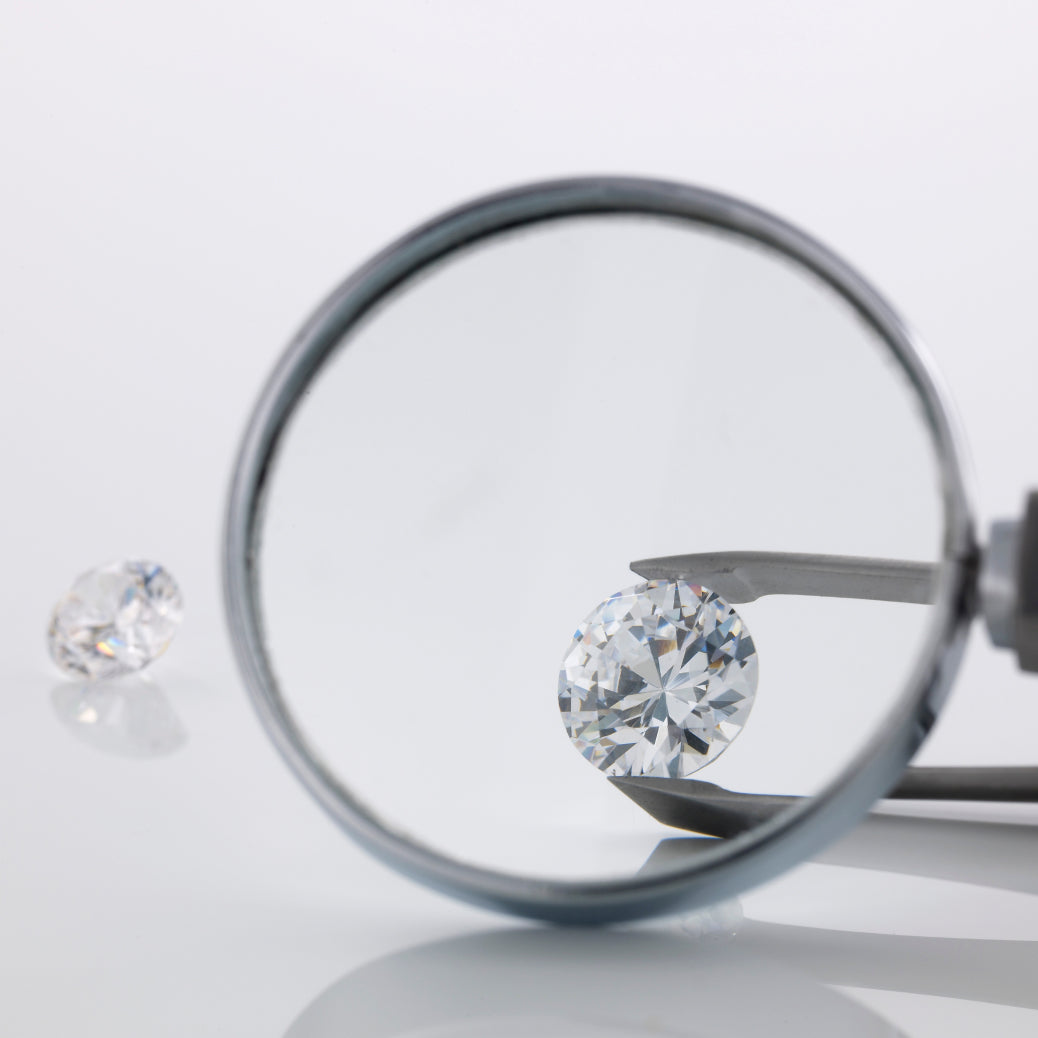

Clarity
Clarity is a measure of the purity and rarity of the stone.
-

Color
Color refers to the natural tint inherent in white diamonds.
-

Carat
Carat denotes the weight of a diamond.

Diamond Cut Chart
This chart evaluates how well a diamond has been cut, impacting its symmetry, proportion, and ability to reflect light. Grades range from excellent to poor. An excellent cut provides optimal brilliance and fire, while lower grades result in less sparkle. The chart aids in understanding the cut's influence on a diamond's beauty.
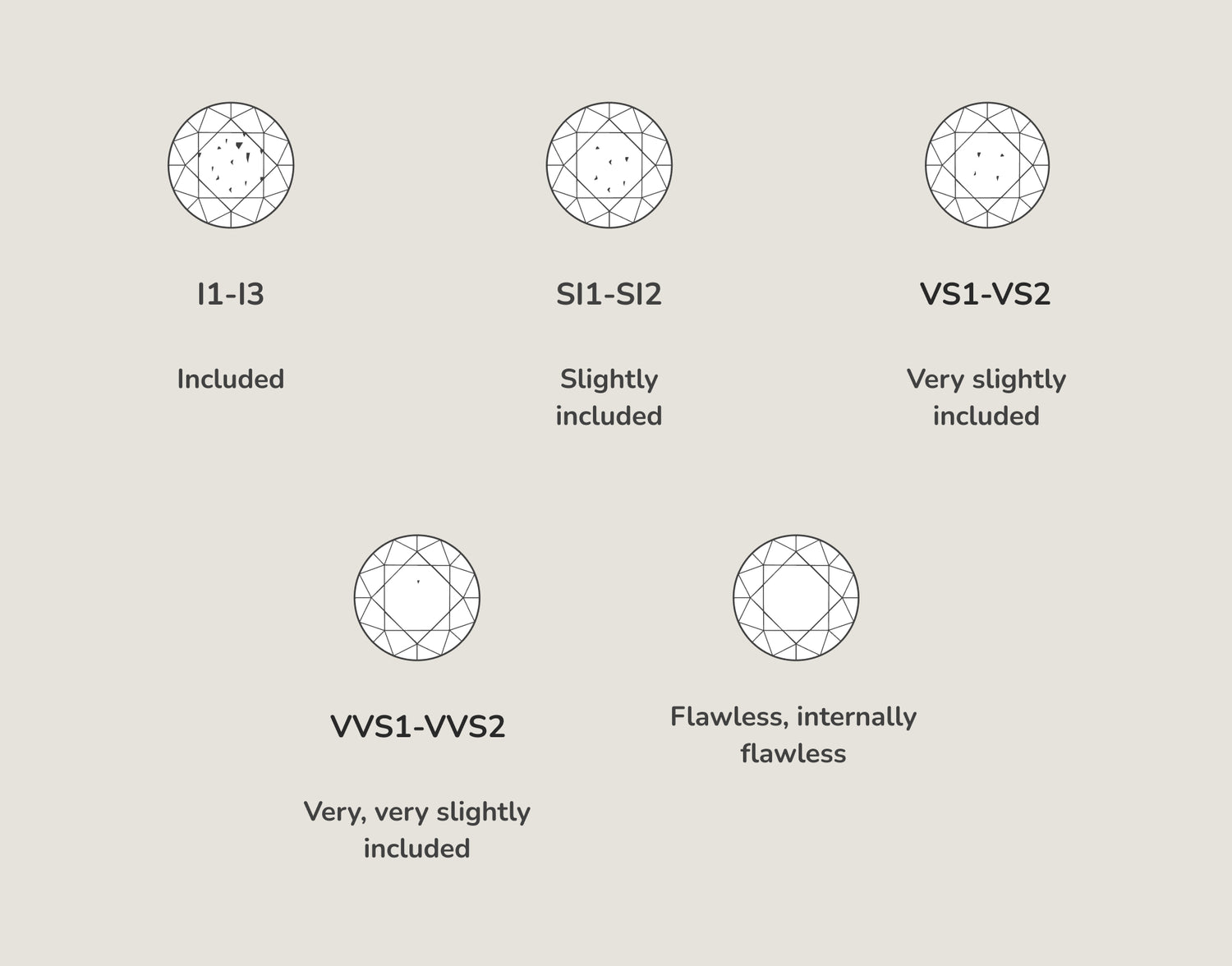
Diamond Clarity Chart
The diamond clarity chart defines the level of natural imperfections in diamonds, known as inclusions and blemishes. Ranging from flawless (no inclusions) to included (visible inclusions), this chart assists in evaluating how clarity affects a diamond's purity and brilliance.

Diamond Color Chart
The diamond color chart categorizes diamonds from the highest rating, D (colorless), to Z (light color). Color grades affect a diamond's appearance and value. Colorless diamonds, graded D-F, are rare and most valuable, while grades G-J are near-colorless, offering good value with slight color.
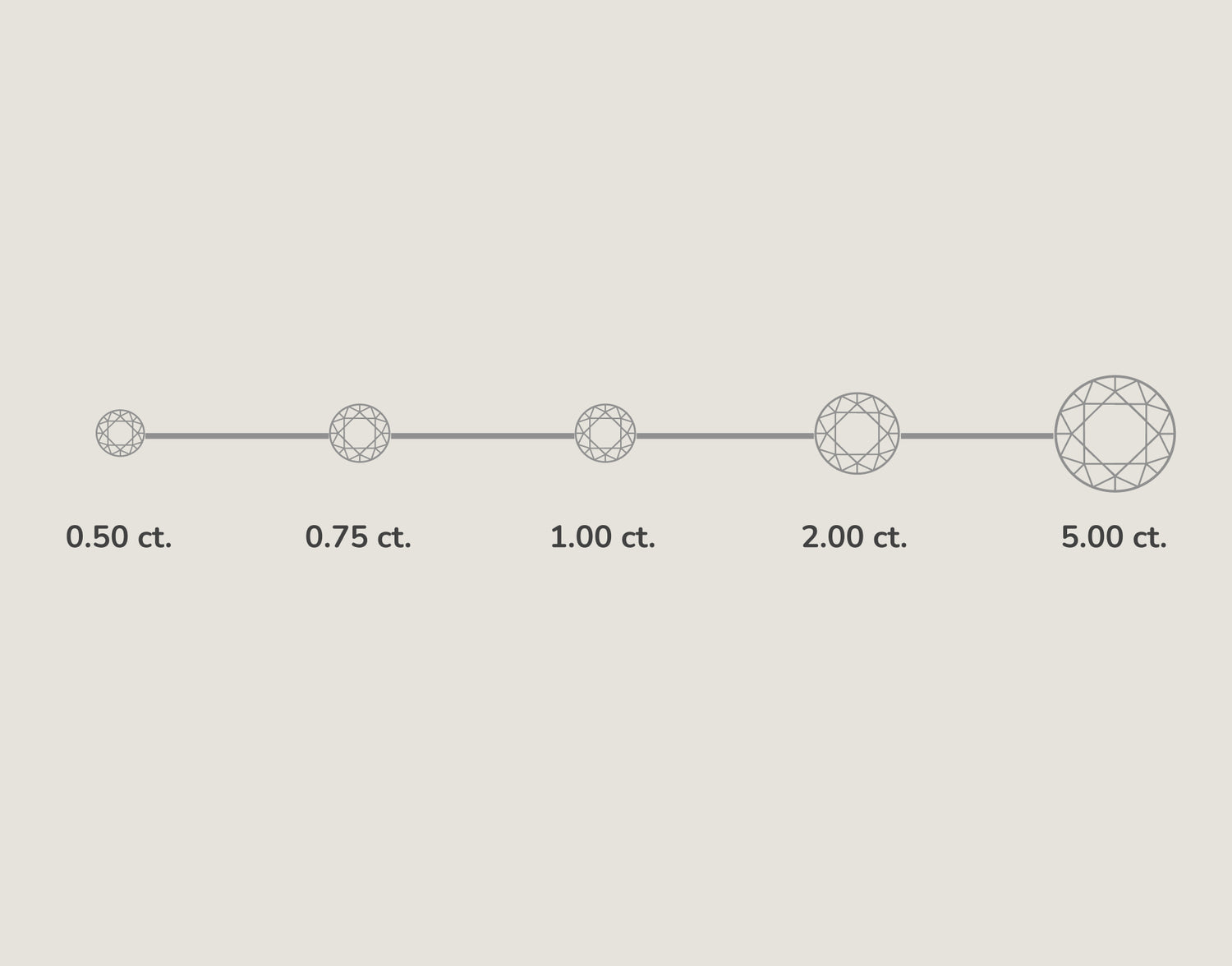
Diamond Carat Chart
A diamond carat chart illustrates the size differences between diamonds of various weights. Carats measure weight, not size, but larger carats typically mean a bigger diamond. This chart helps visualize how diamonds of different carat weights appear in size compared to one another.



